Azure automation accounts allow for the offloading of scripts etc (runbooks) into Azure rather than requiring on-premise scheduled tasks etc. All the necessary components are in a single location making depedency mapping etc much easier.
Azure Automation (offical documents)
Process automation in Azure Automation allows you to create and manage PowerShell, PowerShell Workflow, and graphical runbooks. For details, see Azure Automation runbooks.
Automation executes your runbooks based on the logic defined inside them. If a runbook is interrupted, it restarts at the beginning. This behavior requires you to write runbooks that support being restarted if transient issues occur.
Starting a runbook in Azure Automation creates a job, which is a single execution instance of the runbook. Each job accesses Azure resources by making a connection to your Azure subscription. The job can only access resources in your datacenter if those resources are accessible from the public cloud.
Azure Automation assigns a worker to run each job during runbook execution. While workers are shared by many Automation accounts, jobs from different Automation accounts are isolated from one another. You can't control which worker services your job requests.
When you view the list of runbooks in the Azure portal, it shows the status of each job that has been started for each runbook. Azure Automation stores job logs for a maximum of 30 days.
The following diagram shows the lifecycle of a runbook job for PowerShell runbooks, PowerShell Workflow runbooks, and graphical runbooks.
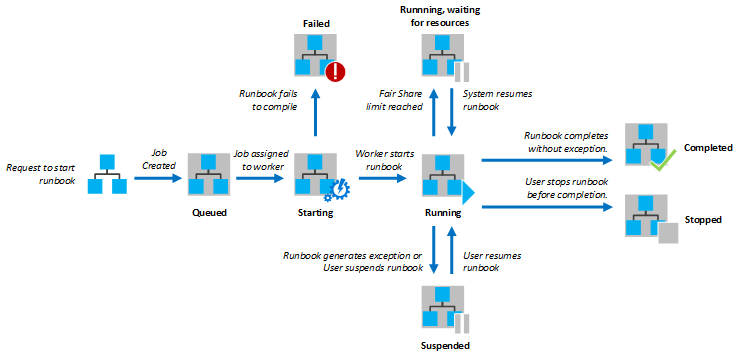
Runbook execution environment
Runbooks in Azure Automation can run on either an Azure sandbox or a Hybrid Runbook Worker.
When runbooks are designed to authenticate and run against resources in Azure, they run in an Azure sandbox. Azure Automation assigns a worker to run each job during runbook execution in the sandbox. While workers are shared by many Automation accounts, jobs from different Automation accounts are isolated from one another. Jobs using the same sandbox are bound by the resource limitations of the sandbox. The Azure sandbox environment doesn't support interactive operations. It prevents access to all out-of-process COM servers, and it doesn't support making WMI calls to the Win32 provider in your runbook. These scenarios are only supported by running the runbook on a Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker.
You can also use a Hybrid Runbook Worker to run runbooks directly on the computer that hosts the role and against local resources in the environment. Azure Automation stores and manages runbooks and then delivers them to one or more assigned computers.
Automation Hybrid Runbook Worker overview
Runbooks in Azure Automation might not have access to resources in other clouds or in your on-premises environment because they run on the Azure cloud platform. You can use the Hybrid Runbook Worker feature of Azure Automation to run runbooks directly on the machine hosting the role and against resources in the environment to manage those local resources. Runbooks are stored and managed in Azure Automation and then delivered to one or more assigned machines.
Azure Automation provides native integration of the Hybrid Runbook Worker role through the Azure virtual machine (VM) extension framework. The Azure VM agent is responsible for management of the extension on Azure VMs on Windows and Linux VMs, and Azure Connected Machine agent] on Non-Azure machines including Azure Arc-enabled Servers and Azure Arc-enabled VMware vSphere (preview).
Specific Configuration
Azure Automation account
The Automation Account (AA) consists of all the elements required to store, run and manage the scripts:
AA Account: Subscription: Resource Group:
Runbooks
Each script is an individual runbook running on a job on schedule.
Each runbook is named appropriately with the relevant configuration it requires.
Hybrid Worker Groups
One or more Hybrid Worker (HW) groups can be created to run the scripts against on-premises infrastructure
Group Name: Hybrid Workers: Hybrid Credentials:
The Hybrid worker account should be created on-premise and syncronised with AAD to ensure it has the correct access required.
To update the password to the HW account navigate to AA > Credentials.
Multiple VMs can be added to the HWG for redundancy, by default the AA account will use any available worker.
Storage Account
As some scripts require resources such as log files create a storage account within the same resource group as the AA account.
The Hybrid Worker account is then given access to the share.